Difference between revisions of "Historical:Partial Panoramas using ROI in PTViewer"
(Use this method if you have a panorama that is not fully 360°x180°, and you still want to use PTViewer to immerse your audience into your panorama) |
m (some typo's fixed and added equirectangular demand) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
If you have a panorama that is not fully 360�x180�, and you still want to use PTViewer to immerse your audience into your panorama, there are a few methods to do that. | If you have a panorama that is not fully 360�x180�, and you still want to use PTViewer to immerse your audience into your panorama, there are a few methods to do that. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 5: | ||
To avoid this, it is possible to use a Region Of Interest picture (ROI) to display the panorama. This will only download the partial panorama. We will have to tell PTViewer where to place the picture, and how far the user may pan left and right, and how much they can tilt up and down. | To avoid this, it is possible to use a Region Of Interest picture (ROI) to display the panorama. This will only download the partial panorama. We will have to tell PTViewer where to place the picture, and how far the user may pan left and right, and how much they can tilt up and down. | ||
| − | == Gathering Information | + | Note this is not an explanation of the syntax of PTViewer, rather a tutorial on how to calculate the different parameters. For the syntax on PTViewer you can visit : [http://webuser.fh-furtwangen.de/~dersch/PTVJ/doc.html PTViewer Documentation] |
| + | |||
| + | Good luck. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Richard Korff | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Gathering Information == | ||
[[Image:ROI_image1.jpg|Sample image]] | [[Image:ROI_image1.jpg|Sample image]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 20: | ||
* Position of the horizon from the top of the picture (Horizon pos) 227 px | * Position of the horizon from the top of the picture (Horizon pos) 227 px | ||
| − | From the | + | The picture must have [http://www.panotools.info/mediawiki/index.php?title=Equirectangular equirectangular] projection |
| + | |||
| + | From the stitcher we should be able to get the Horizontal Field of View (HFOV). In this case 160� | ||
From these 4 numbers we should be able to calculate the parameters necessary for PTViewer to display a partial panorama. | From these 4 numbers we should be able to calculate the parameters necessary for PTViewer to display a partial panorama. | ||
== Calculating the parameters for PTViewer == | == Calculating the parameters for PTViewer == | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:ROI_image2.jpg|Sample overview]] | [[Image:ROI_image2.jpg|Sample overview]] | ||
| + | |||
Since we know the ROI Width of the picture as well as the Horizontal Field of View (HFOV), we can calculate the field of view for 1 pixel. | Since we know the ROI Width of the picture as well as the Horizontal Field of View (HFOV), we can calculate the field of view for 1 pixel. | ||
| − | In this case | + | In this case |
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | 160� / 800 pixels = 0.2�/px | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | We need this number to convert from pixels to degrees and vice versa. You need an accuracy of a couple of decimals otherwise it won't work. | |
| − | |||
| − | The objective is to place the ROI picture inside the 360�x180� panorama with the horizon in the ROI image over the horizontal 0� line, and the middle of the ROI image | + | The objective is to place the ROI picture inside the 360�x180� panorama with the horizon in the ROI image over the horizontal 0� line of the pano, and the middle of the ROI image in the middle of the panorama. |
== pwidth and pheight == | == pwidth and pheight == | ||
To do that we first need to calculate the total size of the panorama image, of which the ROI image is a part of. | To do that we first need to calculate the total size of the panorama image, of which the ROI image is a part of. | ||
| − | The calculation is | + | The calculation is done by using the number of degrees per pixel. |
| + | Since we know the degrees, we can calculate the number of pixels. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
Panorama Width (Pwidth) = 360� / 0.2�/px = 1800 px | Panorama Width (Pwidth) = 360� / 0.2�/px = 1800 px | ||
Panorama Height (Pheigth) = 180� / 0.2/px = 900 px | Panorama Height (Pheigth) = 180� / 0.2/px = 900 px | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | == x and y | + | == x and y insertion point == |
| − | To calculate the x and y | + | To calculate the x and y position of the insertion point (the point where the picture needs to be placed) |
| − | We | + | We can calculate that by taking half of the panorama height and subtracting the horizon position in the ROI. |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | Y position of the insertion point = 900px/2 � 227px = 223px | |
| − | Y | + | </pre> |
Similarly we can calculate the x offset. | Similarly we can calculate the x offset. | ||
| − | In most circumstances, you either don�t know, or don�t care about the direction the picture was taken. In that case it is good practice to place the ROI in the middle of the large pano where 0� is the middle of the picture. | + | In most circumstances, you either don�t know, or don�t care about the direction the picture was taken. In that case it is good practice to place the ROI in the middle of the large pano where 0� is the middle of the picture. You can do this by taking half of the total panorama width and subtracting half the size of the picture |
| − | You can do this by taking half of the total panorama width | + | <pre> |
| − | + | X position of the insertion point = 1800px/2 � 800px/2 = 500 px | |
| − | X | + | </pre> |
| − | == panmin, panmax, tiltmin and tiltmax | + | == panmin, panmax, tiltmin and tiltmax == |
| − | To limit the freedom the user has in moving around your pano, you want to restrict the pan and tilt angles. | + | To limit the freedom the user has in moving around your pano, you want to restrict the pan and tilt angles. To calculate this is relatively easy with the information we have gathered above. |
| − | |||
| − | To calculate this is relatively easy with the information we have gathered above. | ||
The pan and tilt angles are calculated in degrees. | The pan and tilt angles are calculated in degrees. | ||
Because the ROI is horizontally in the middle, you may pan half the width of the image to the left and right, converted to degrees. | Because the ROI is horizontally in the middle, you may pan half the width of the image to the left and right, converted to degrees. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
Minimum pan = -800px/2 * 0.2�/px = -80� | Minimum pan = -800px/2 * 0.2�/px = -80� | ||
Maximum pan = 800px/2 * 0.2�/px = 80� | Maximum pan = 800px/2 * 0.2�/px = 80� | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | The | + | The minimum tilt is calculated as the height of the ROI minus the position of the horizon, converted to degrees. |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | Minimum tilt = -(541px � 227px) * 0.2�/px = -62.8� => -62� | |
| − | + | </pre> | |
| − | + | The maximum tilt is calculated as the position of the horizon, converted to degrees. | |
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Maximum tilt = 227px * 0.2�/px = 45.4� => 45� | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Because ptviewer does not take fractions of degrees, you throw away the fraction. | |
| − | + | Using these numbers in PTViewer should give you a good partial panorama. If you see blank space at the edges of the panorama, you may want to make a 1 degree change to the minimum and maximum pan and tilt untill it does not show up anymore. | |
| + | |||
| + | Have fun. | ||
Revision as of 18:28, 20 March 2005
If you have a panorama that is not fully 360�x180�, and you still want to use PTViewer to immerse your audience into your panorama, there are a few methods to do that.
You can expand your Panorama with blank space around, and use the normal way of displaying a panorama in PTViewer. The disadvantage of this is that if you put this picture online, the download times can be significantly longer because of all the blank space.
To avoid this, it is possible to use a Region Of Interest picture (ROI) to display the panorama. This will only download the partial panorama. We will have to tell PTViewer where to place the picture, and how far the user may pan left and right, and how much they can tilt up and down.
Note this is not an explanation of the syntax of PTViewer, rather a tutorial on how to calculate the different parameters. For the syntax on PTViewer you can visit : PTViewer Documentation
Good luck.
Richard Korff
Gathering Information
From the ROI picture we need to get some basic information :
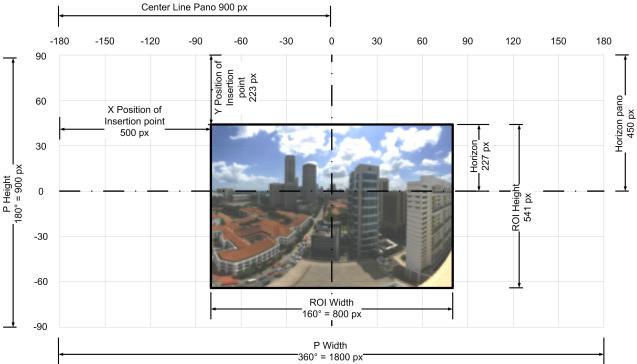
- Width in pixels (ROI Width) 800 px
- Height in pixels (ROI Height) 541 px
- Position of the horizon from the top of the picture (Horizon pos) 227 px
The picture must have equirectangular projection
From the stitcher we should be able to get the Horizontal Field of View (HFOV). In this case 160�
From these 4 numbers we should be able to calculate the parameters necessary for PTViewer to display a partial panorama.
Calculating the parameters for PTViewer
Since we know the ROI Width of the picture as well as the Horizontal Field of View (HFOV), we can calculate the field of view for 1 pixel.
In this case
160� / 800 pixels = 0.2�/px
We need this number to convert from pixels to degrees and vice versa. You need an accuracy of a couple of decimals otherwise it won't work.
The objective is to place the ROI picture inside the 360�x180� panorama with the horizon in the ROI image over the horizontal 0� line of the pano, and the middle of the ROI image in the middle of the panorama.
pwidth and pheight
To do that we first need to calculate the total size of the panorama image, of which the ROI image is a part of. The calculation is done by using the number of degrees per pixel. Since we know the degrees, we can calculate the number of pixels.
Panorama Width (Pwidth) = 360� / 0.2�/px = 1800 px Panorama Height (Pheigth) = 180� / 0.2/px = 900 px
x and y insertion point
To calculate the x and y position of the insertion point (the point where the picture needs to be placed)
We can calculate that by taking half of the panorama height and subtracting the horizon position in the ROI.
Y position of the insertion point = 900px/2 � 227px = 223px
Similarly we can calculate the x offset. In most circumstances, you either don�t know, or don�t care about the direction the picture was taken. In that case it is good practice to place the ROI in the middle of the large pano where 0� is the middle of the picture. You can do this by taking half of the total panorama width and subtracting half the size of the picture
X position of the insertion point = 1800px/2 � 800px/2 = 500 px
panmin, panmax, tiltmin and tiltmax
To limit the freedom the user has in moving around your pano, you want to restrict the pan and tilt angles. To calculate this is relatively easy with the information we have gathered above. The pan and tilt angles are calculated in degrees.
Because the ROI is horizontally in the middle, you may pan half the width of the image to the left and right, converted to degrees.
Minimum pan = -800px/2 * 0.2�/px = -80� Maximum pan = 800px/2 * 0.2�/px = 80�
The minimum tilt is calculated as the height of the ROI minus the position of the horizon, converted to degrees.
Minimum tilt = -(541px � 227px) * 0.2�/px = -62.8� => -62�
The maximum tilt is calculated as the position of the horizon, converted to degrees.
Maximum tilt = 227px * 0.2�/px = 45.4� => 45�
Because ptviewer does not take fractions of degrees, you throw away the fraction.
Using these numbers in PTViewer should give you a good partial panorama. If you see blank space at the edges of the panorama, you may want to make a 1 degree change to the minimum and maximum pan and tilt untill it does not show up anymore.
Have fun.